- EFTPOS & Point of Sale Solutions
How NFC Mobile Payments Work
Mobile wallets are quickly gaining traction in Australia — but do you understand how the technology actually works?
These days, Australians are using their mobile phones to make money, save money and invest money. You’re probably familiar with how apps like eBay, Gumtree, and Raiz work, and comfortable using at least a couple of them. But what about the technology that lets your customers spend money at your business using their mobile phones?
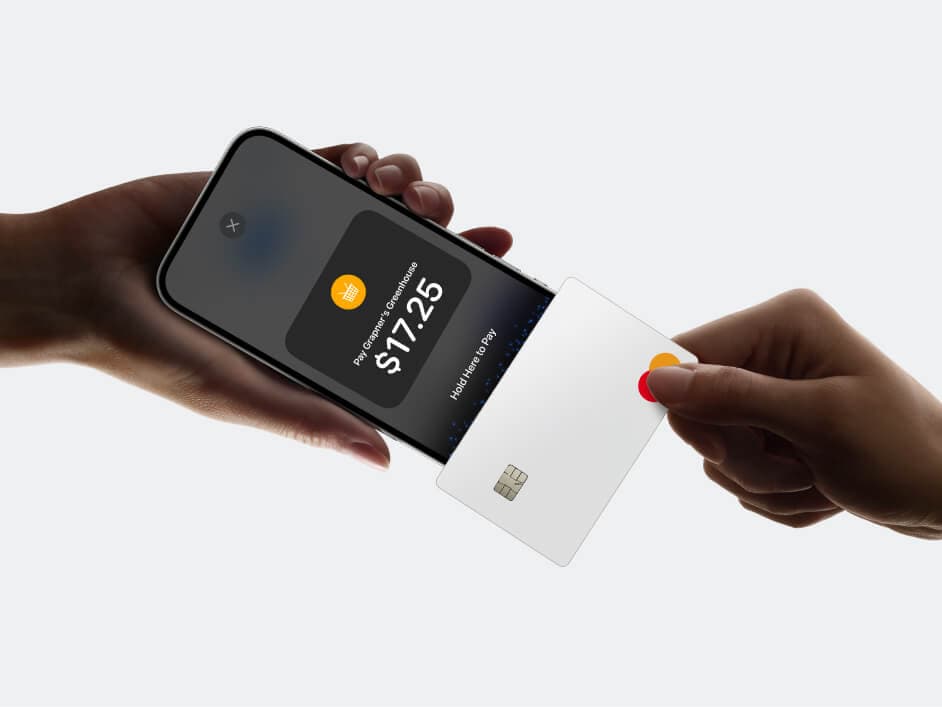
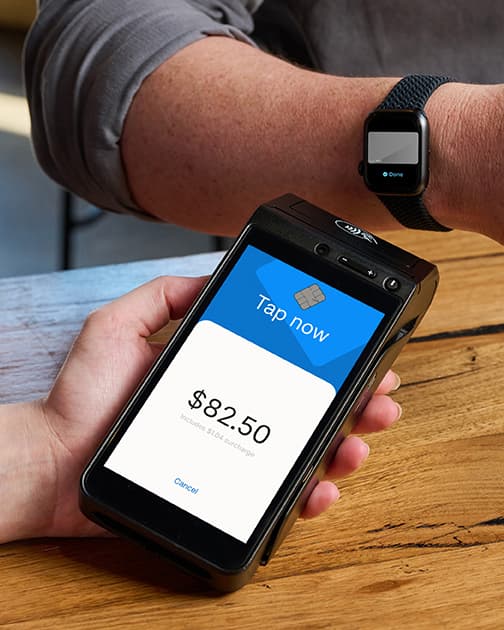
Many of the major tech players have built their own mobile wallets that allow for contactless payment, such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay. These mobile wallets make it possible for a customer to pay for goods or services through their phone, smartwatch, or other device, no physical contact required. It’s a convenient, quick, and sanitary way to take payment.

Australians are increasingly using their mobile devices to pay for goods and services contactlessly.
Take a peek inside your customers’ wallets
A mobile wallet gives your customers the ability to pay via a trusted device. Also known as digital wallets or eWallets, mobile wallets are a driving force behind the “cashless” fintech trend.
There are a couple of key players you should know about.
What is Apple Pay?
Apple Pay is Apple’s own mobile wallet. The Apple Pay mobile wallet works on Apple devices, including the iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch and Mac. When Apple Pay launched back in 2014, it was described as “revolutionary”; Apple Pay promised (and delivered) a secure, simple way to pay via a mobile device.
What is Google Pay?
Google’s mobile wallet, developed shortly after Apple Pay, works on most Android phones. Google Pay was originally known as Android Pay, and is almost an identical offering to its Apple counterpart.
What is Samsung Pay?
Samsung eventually caught up with the pack in 2016, when it released its own mobile wallet: Samsung Pay. As a relatively recent newcomer, Samsung Pay isn’t available in as many countries as Apple Pay or Google Pay. However, it is supported in Australia.
There are a number of other mobile wallets available on the App Store and Google Play Store, including Fitbit Pay and Garmin Pay which work on wearable devices (i.e. smart watches). While there are some minor differences between mobile wallets, the main purpose remains the same: to allow a customer pay contactlessly.
It’s all possible thanks to Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, and if you’re going to accept contactless payments in your business, you should really know how it all works.
What is “contactless payment”?
Contactless payment is exactly what it sounds like: a way of paying without human contact. It’s often described as “tap-and-go” payment. To pay contactlessly, a customer taps their card or trusted device to an EFTPOS terminal. The EFTPOS terminal then reads the credit or debit card information and charges the customer’s account.
Australians use contactless payment more often than any other country in the world; four in five pay contactlessly at least once a week. In fact, Australians are so used to being able to pay contactless that when a business doesn’t accept contactless payments, one third feel inconvenienced (and some will even avoid those businesses altogether).
There are a number of benefits for both the paying customer and the business accepting payment contactlessly.
Transactions are faster
This innovative payment method makes in-store transactions even faster, because customers can simply tap their device instead of inserting it. That means a quicker customer turnover, positioning merchants to make more money in a shorter period of time, and a better customer experience.
The technology behind contactless payments also makes the transaction fast from a technical perspective. We’ll dive deeper into this in just a moment.
Customer information is less visible
Contactless payment is also designed to be safer than traditional payment methods, as a customer’s physical card is never handed over to the person taking payment.
Tapping a card only takes a second or two, meaning the card number is much less visible to strangers. When accepting contactless payment through a mobile device, the card number isn’t visible at all. A customer simply has to tap their device to the EFTPOS terminal.
Mobile wallets are more secure
There’s an extra element of security protecting payments through mobile wallets: tokenization. This is the technology that keeps a customer's bank details safe in their mobile wallet.
Put simply, tokenization is the process of replacing sensitive card data with a series of randomly generated numbers: a “token”. Even if a fraudster managed to get around the protective measures already in place on a mobile device (such as a fingerprint scanner, password or facial recognition technology), they would not be able to access card data.
Want more details? Here’s how it usually works: A customer takes a picture of their credit or debit card, and loads it into their mobile wallet. Their mobile wallet provider sends the details to the card’s issuing bank or network, where the details are then replaced with a random token. This token is then sent back to the mobile wallet provider, and from there the token is programmed into the mobile wallet – effectively rendering the mobile wallet useless to fraudsters.
Contactless payments are safer
On top of being faster and safer, accepting payments contactlessly is a more sanitary option. The COVID-19 pandemic has made many people realise just how often they come into close contact with strangers every day, and passing money back and forth is one of the ways they do that. The average banknote lasts about eight years before it deteriorates and becomes unfit for use — consider how many hands may touch a banknote throughout its lifespan.
By using contactless payment options, customers can pay for your products or services without direct contact, keeping themselves and your business safe.
Now you know the benefits of contactless payment, it’s important to explain how NFC technology makes it possible.
What is NFC technology, and how does it work?
Do you have your Alexa or Google device connected to your smartphone via Bluetooth, or your computer connected to your printer wirelessly over Wi-Fi? These devices recognise each other, and communicate over radio waves. NFC technology works in a similar way.
When a customer makes a purchase using NFC technology, their card or device transmits account information via radio waves to the payment processor. Once received, the processor uses the information to complete the transaction.
You may be wondering how the payment processor is able to charge the customer’s card without ever physically touching it. The answer is in the name of the technology: “near field.” The device transmitting payment information (i.e. the customer’s card or mobile device) has to be within a few centimetres of the device on the receiving end (i.e. your EFTPOS terminal). It’s this requirement for close proximity that makes contactless payments a secure option. If the transaction could be completed from further away, that could lead to the payment processor charging the wrong customer’s card.
An advantage of NFC technology is that it processes payments incredibly quickly.
The payment processor has inductive coupling capabilities, which means it can automatically recognise an appropriate device without a manual connection. When a customer pays for something with NFC technology, it takes a few seconds or less — allowing for a frictionless, speedy exchange.
Accept payments the way your customers expect
Now that you understand how NFC technology works, you can feel more comfortable accepting contactless payments from your customers.
At Zeller, we're reimagining business banking. Our next-gen EFTPOS Terminal accepts tapped, dipped, and swiped payments, as well as mobile wallets, so you can accept payment however it is most convenient for your customer.